Defining structural element properties
 |
In order to start assigning structural properties, choose "Structural
Property" item in  menu.
"Property" dialog appears, and the current state of their assignment
are displayed in the main window. The element properties are defined and
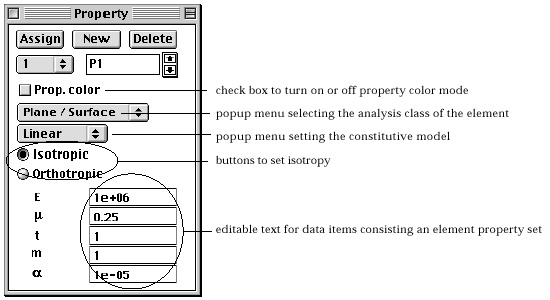
assigned by the data unit called element property set. A set consists
of many data items, all of which are displayed on "Property"
dialog. Structural element properties may include geometric characteristics
as well as material properties. The items differ depending on the subject
of analysis, or analysis class of the element as described
below. menu.
"Property" dialog appears, and the current state of their assignment
are displayed in the main window. The element properties are defined and
assigned by the data unit called element property set. A set consists
of many data items, all of which are displayed on "Property"
dialog. Structural element properties may include geometric characteristics
as well as material properties. The items differ depending on the subject
of analysis, or analysis class of the element as described
below.
|
> Analysis class of element
 |
The first popup menu in "Property" dialog is provided
to enable mixing different types of structures in one analysis, as explained
in the next section. Using this menu, you can select the type of analysis-related
characteristics to impose on the element. It is termed here as "Analysis
class of element." Each item of the popup menu represents an analysis
class of an element. |
|
"Plane/Surface": plane stress, plane strain,
axisymmetric, plate bending, and shell element.
|
|
"Solid": 3-d solid element.
|
|
"Truss": 2-d or 3-d truss element.
|
|
"Frame": 2-d or 3-d frame element.
|
|
"Interface": interface or gap
element
|
|
"Slip Bar": slip bar element
|
|
"Embedded bar": embedded bar
element
|
|
"Heat": heat conduction element
|
Only classes compatible for the current project are selectable. In case of
frame analysis, for example, "Truss" and "Frame" items are
selectable, and others are disabled.
> Constitutive model
The second popup menu in "Property" dialog is to select the constitutive
model. This is applicable for material nonlinear analysis
of structures. For linear analysis, the menu contains only
"Linear" item. The current version of VisualFEA supports only those
nonlinearities shown as the menu items. The items vary depending
on the analysis class of element as described in the previous
section. For "Plane/Surface" and "Solid", the following
items are available.
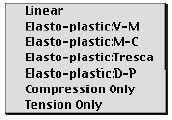 |
"Linear": linear elastic model.
|
|
"Elasto-plastic:V-M": Elasto-plastic
model with Von Mises yield criterion.
|
|
"Elasto-plastic : M-C": Elasto - plastic model
with Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion.
|
|
"Elasto-plastic:Tresca": Elasto-plastic model with
Tresca yield criterion.
|
|
"Elasto-plastic : D - P": Elasto-plastic model
with Drucker-Prager yield criterion.
|
|
"Compression Only": Linear constitutive relationship
for compression, and no stress for tension.
|
|
"Tension Only": Linear constitutive relationship
for tension, and no stress for compression. The following are the items
available for interface elements.
|
|
"Linear Interface": linear elastic properties defined
in the longitudinal and the thickness direction respectively.
|
|
"No tension slip": The interface delivers compressive
normal force across the element, but not tensile force. The maximum resistance
against slippage between the two faces across the element is defined by
the friction coefficient. The maximum resisting stress is obtained by
normal stress multiplied by the friction coefficient.
|
 |
"No compression slip": The interface delivers tensile
normal force across the element, but not compressive force. The maximum
resistance against slippage between the two faces across the element is
defined by friction coefficient. The maximum resisting stress is obtained
by normal stre s s multiplied by the friction coefficient.
|
|
"Gap": The interface models a gap between two faces.
No force is delivered between the two faces until the gap is diminished
by deformation. The following are the items available for slip bar elements.
|
 |
"Linear bonding": The bonding between the slip
bar and the surrounding body is represented by linear elastic model .
|
|
"Nonlinear bonding": The bonding between the slip
bar and the surrounding body is represented by nonlinear stress-strain
relationship.
|
> Isotropy of the properties
The element properties can be defined as either isotropic or orthotropic
using the radio buttons in "Property" dialog. In case the properties
are defined as orthotropic, there appear more items in the dialog as shown in
the following figure.
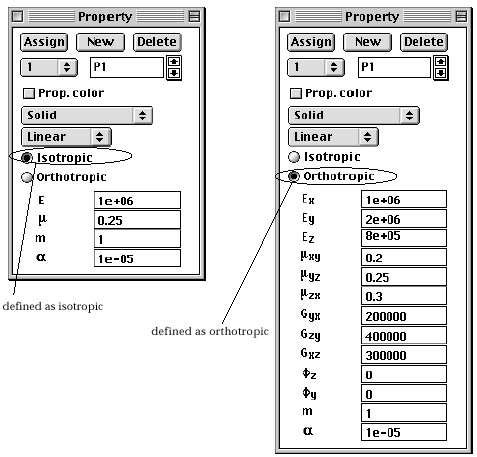
<Data items for isotropic materials and for orthotropic ones>
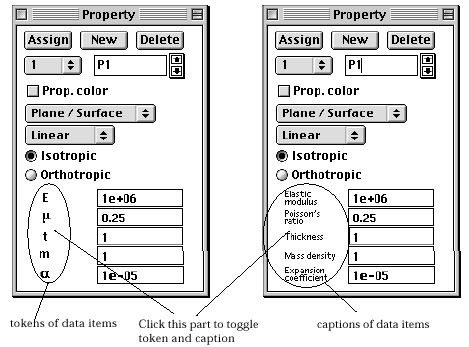
> Data items of element properties
An element property set consists of a number of data items, which vary depending
on the analysis subject, analysis class of the element and the isotropy. As
you alter the popup menu items or radio buttons on "Property" dialog,
you will notice that the dialog expands or shrinks in its size to accommodate
the changing data items properly. Each data item is denoted by a simple token
or by a caption. This denotation of data items can be toggled by clicking the
part of the dialog as shown in the figure below..
![]()

